
- #Powershell move item overwrite how to#
- #Powershell move item overwrite install#
- #Powershell move item overwrite code#
- #Powershell move item overwrite windows#
After calling copy-item, you would have to delete the original folder in a second step. It works because it would not replace existing folders but just appends them with new stuff. As a workaround, you could use copy-item: Copy-Item c:\test -Destination c:\tmp -Force -Recurse. When you move an item, it is added to the new location and deleted from its original. For example, it can move a file or subdirectory from one directory to another or move a registry subkey from one key to another. The locations must be supported by the same provider. The Move-Item cmdlet moves an item, including its properties, contents, and child items, from one location to another location. Powershell: Move all files from folders and subfolders into single folder. Note that this is the same behavior for the. I need to copy individual files to multiple domain computers and over write the existing files This is essentially what the thoughtful Microsoft engineers have done for you through their UI for merging folders and overwriting files. # Create-NewFile.So I have this PS script which I found on here that works great, but now i need some changes made to it for another task. After saving the script, run it in PowerShell to test. Make sure to change the value of the $path variable should you want to change the file’s output location.
#Powershell move item overwrite code#
If the file exists, the script shows a message and does not attempt to make the file anymore.Ĭopy the code below and save it in a file called Create-NewFile.ps1. To avoid the “ file already exists” error, the script checks if the file already exists before creating it. This example is a typical use-case to create files at a specified location.
#Powershell move item overwrite how to#
Related: How to Use the PowerShell Test-Path Cmdlet Example: Creating A File If The File Does Not Exist Using Test-Path in PowerShell to check if a file exists Otherwise, the result would be False, as you can see from the screenshot below. When you run the command above in PowerShell, the result returns True if the file exists. Test-Path -Path C:\temp\important_file.txt -PathType Leaf Note that the -PathType Leaf part tells the cmdlet to check for a file and not a directory explicitly.
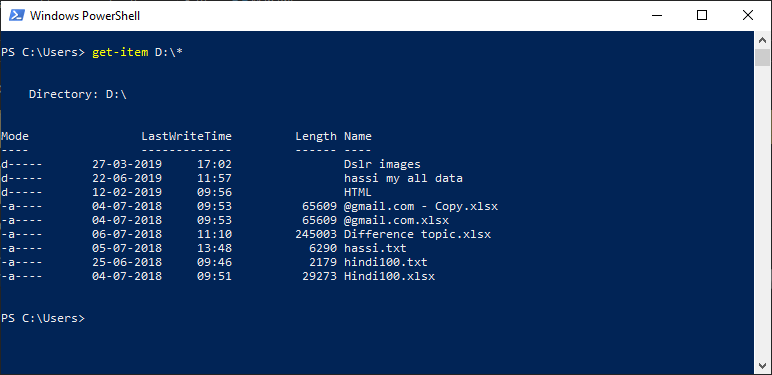
Test-Path -Path -PathType Leafįor example, if you need to check such a file with the name C:\temp\important_file.txt exists, use the code below. The result indicates whether the file exists or not.īelow is the basic syntax to make the Test-Path cmdlet work with checking a file. When using this cmdlet to test whether a file exists, the result is true or false. The first way is the Test-Path cmdlet, specifically designed to determine whether a path or file exists. There will be examples and demos of each of these three methods, including how to use them with error handling. Using these three methods differ in usage, but the concept and end goal are the same.
This article covers three methods with which to use PowerShell to check if a file exists.
#Powershell move item overwrite install#
Related: How to Download and Install PowerShell 7 on Windows, Linux, and macOS Using PowerShell to Check If File Exists Whether you’re using Windows, Linux, or macOS, you’ll be fine as long as you have PowerShell installed. The commands and scripts in this article apply to both PowerShell editions.
#Powershell move item overwrite windows#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
